-
 Paterson takes five wickets as Pakistan bowled out for 211
Paterson takes five wickets as Pakistan bowled out for 211
-
Kremlin cautions on 'hypotheses' over plane crash

-
 Pakistan military convicts 60 more civilians of pro-Khan unrest
Pakistan military convicts 60 more civilians of pro-Khan unrest
-
Turkey lowers interest rate to 47.5 percent

-
 Syria authorities launch operation in Assad stronghold
Syria authorities launch operation in Assad stronghold
-
Record number of migrants lost at sea bound for Spain in 2024: NGO

-
 Kohli called out over shoulder bump with Konstas during fourth Test
Kohli called out over shoulder bump with Konstas during fourth Test
-
Rural communities urged to flee east Australia bushfire

-
 Sri Lanka train memorial honours tsunami tragedy
Sri Lanka train memorial honours tsunami tragedy
-
S. Korea's opposition moves to impeach acting president

-
 'We couldn't find their bodies': Indonesian tsunami survivors mourn the dead
'We couldn't find their bodies': Indonesian tsunami survivors mourn the dead
-
Lakers pip Warriors after another LeBron-Curry classic

-
 India readies for 400 million pilgrims at mammoth festival
India readies for 400 million pilgrims at mammoth festival
-
Nepal hosts hot air balloon festival

-
 Asia stocks up as 'Santa Rally' persists
Asia stocks up as 'Santa Rally' persists
-
Tears, prayers as Asia mourns tsunami dead 20 years on

-
 Sydney-Hobart yacht crews set off on gale-threatened race
Sydney-Hobart yacht crews set off on gale-threatened race
-
Key public service makes quiet return in Gaza

-
 Fearless Konstas slams 60 as Australia take upper hand against India
Fearless Konstas slams 60 as Australia take upper hand against India
-
Hungry Sabalenka ready for more Slam success

-
 Mass jailbreak in Mozambique amid post-election unrest
Mass jailbreak in Mozambique amid post-election unrest
-
Bridges outduels Wembanyama as Knicks beat Spurs

-
 2004 Indian Ocean tsunami: what to know 20 years on
2004 Indian Ocean tsunami: what to know 20 years on
-
Asia to mourn tsunami dead with ceremonies 20 years on

-
 Syrians protest after video of attack on Alawite shrine
Syrians protest after video of attack on Alawite shrine
-
Russian state owner says cargo ship blast was 'terrorist attack'

-
 Crisis-hit Valencia hire West Brom's Corberan as new boss
Crisis-hit Valencia hire West Brom's Corberan as new boss
-
Suriname ex-dictator and fugitive Desi Bouterse dead at 79

-
 Syria authorities say torched 1 million captagon pills
Syria authorities say torched 1 million captagon pills
-
Pope calls for 'arms to be silenced' across world

-
 32 survivors as Azerbaijani jet crashes in Kazakhstan
32 survivors as Azerbaijani jet crashes in Kazakhstan
-
Pakistan air strikes kill 46 in Afghanistan, Kabul says

-
 Liverpool host Foxes, Arsenal prepare for life without Saka
Liverpool host Foxes, Arsenal prepare for life without Saka
-
Zelensky condemns Russian 'inhumane' Christmas attack on energy grid

-
 Sweeping Vietnam internet law comes into force
Sweeping Vietnam internet law comes into force
-
Pope kicks off Christmas under shadow of war

-
 Catholics hold muted Christmas mass in Indonesia's Sharia stronghold
Catholics hold muted Christmas mass in Indonesia's Sharia stronghold
-
Japan's top diplomat in China to address 'challenges'

-
 Thousands attend Christmas charity dinner in Buenos Aires
Thousands attend Christmas charity dinner in Buenos Aires
-
Demand for Japanese content booms post 'Shogun'

-
 As India's Bollywood shifts, stars and snappers click
As India's Bollywood shifts, stars and snappers click
-
Mystery drones won't interfere with Santa's work: US tracker

-
 Djokovic eyes more Slam glory as Swiatek returns under doping cloud
Djokovic eyes more Slam glory as Swiatek returns under doping cloud
-
Australia's in-form Head confirmed fit for Boxing Day Test

-
 Brazilian midfielder Oscar returns to Sao Paulo
Brazilian midfielder Oscar returns to Sao Paulo
-
'Wemby' and 'Ant-Man' to make NBA Christmas debuts

-
 US agency focused on foreign disinformation shuts down
US agency focused on foreign disinformation shuts down
-
On Christmas Eve, Pope Francis launches holy Jubilee year

-
 'Like a dream': AFP photographer's return to Syria
'Like a dream': AFP photographer's return to Syria
-
Chiefs seek top seed in holiday test for playoff-bound NFL teams


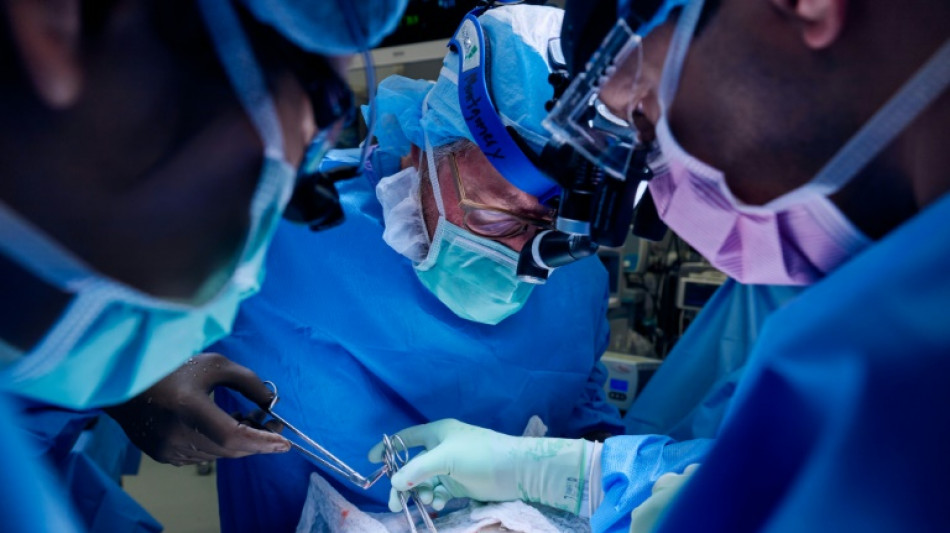
US surgeons transplant pig kidney to live patient for second time
Surgeons in the United States have transplanted a modified pig kidney into a living person for the second time, a hospital said Wednesday, celebrating an advance in animal-to-human organ transplants.
The procedure at NYU Langone Health in New York was carried out in April on Lisa Pisano, 54, who had suffered heart failure and end-stage kidney disease, with doctors giving her just weeks to live barring some kind of medical intervention.
Surgeons implanted a mechanical heart pump in Pisano days before the transplant, which NYU Langone Health said was a world-first for this combined procedure.
In addition to the gene-edited kidney, doctors also -- for what the hospital said was the first time on a living patient -- transplanted the pig's thymus gland, which helps "educate" the immune system and reduce the chance of organ rejection.
Lead surgeon Dr Robert Montgomery told reporters Wednesday the operation was a "milestone in our journey to make life-saving organs available to anyone who needs them."
Montgomery, who also carried out the world's first gene-edited pig-to-human kidney transplant on a brain-dead person in 2021, said the latest operation will "bring closer the possibility that no one will have to die, waiting for someone else to die, so they can be saved."
The first-ever transplant of a pig kidney into a living patient was carried out in March at Massachusetts General Hospital on a 62-year-old man.
Xenotransplants -- a transplant of an organ between different species -- have been hailed as a potential solution for in-need patients amid a chronic shortage of organ donors.
However, the human body can reject animal organs, meaning they must be genetically modified to ensure they will be compatible, reducing risk for the patient.
Genetically modified pig hearts were transplanted in 2023 into two patients at the University of Maryland, but both survived less than two months.
Pisano, a grandmother from New Jersey, said she had "exhausted all other resources" before choosing to go ahead with the procedure.
Doctors said it could have taken years for her to find a match for a human kidney transplant, with her body rejecting available donors, according to a hospital statement.
"I said the worst case scenario, if it doesn't work, it might work for the next person. You know, at least somebody's going to benefit from it," Pisano said.
She has shown no signs of organ rejection almost two weeks later, Montgomery said, adding that her kidney function was "perfect."
A.Magalhes--PC




